After overcoming the hurdles of delays due to COVID-19 and budget overruns, NASA has finally given the green light to the Dragonfly rotorcraft mission.
This autonomously piloted, nuclear-powered rotorcraft is set to embark on a groundbreaking journey to Saturn’s largest moon, Titan, in 2028.

Artist’s concept of the Dragonfly rotorcraft (NASA/JHU-APL)
Why Titan?
Titan is no ordinary celestial body. Located about 746 million miles from Earth, it is the second largest moon in our solar system and the only one with a thick atmosphere besides Earth. But what makes Titan truly unique is its organic chemistry. With an atmosphere rich in nitrogen and methane, it is a haven for scientists who want to understand the building blocks of life.
CLICK TO GET KURT’S FREE CYBERGUY NEWSLETTER WITH SECURITY ALERT, QUICK VIDEO TIPS, TECHNICAL REVIEWS AND SIMPLE HOW-TO’S TO MAKE YOU SMARTER

Artist’s concept of the Dragonfly rotorcraft (NASA/JHU-APL)
MORE: UNFORGETTABLE GIFTS FOR MOTHER’S DAY 2024
Research challenges
Titan’s wetlands, made up of petroleum byproducts, present a significant challenge for exploration. Traditional rovers won’t do well there. Enter the Dragonfly, a rotorcraft powered by a radio thermal generator. It flies using aluminum/titanium rotors, designed to skim across Titan’s landscape, conducting geological surveys and searching for biosignatures.

Artist’s concept of the Dragonfly rotorcraft (NASA/JHU-APL)
MORE: HOW THE DREAM CHASER SPACE PLANE PLANS TO SHAKE SPACE TRAVEL IN THE FUTURE
Dragonfly’s Quest for Life
Dragonfly’s mission is to travel to multiple locations on Saturn’s moon, Titan, to detect signs of life. The spacecraft will study the surface and below it, looking for organic compounds and indicators of life. Equipped with a neutron spectrometer, a drilling mechanism and a mass spectrometer, Dragonfly will allow researchers to comprehensively analyze Titan’s complex organic chemistry.
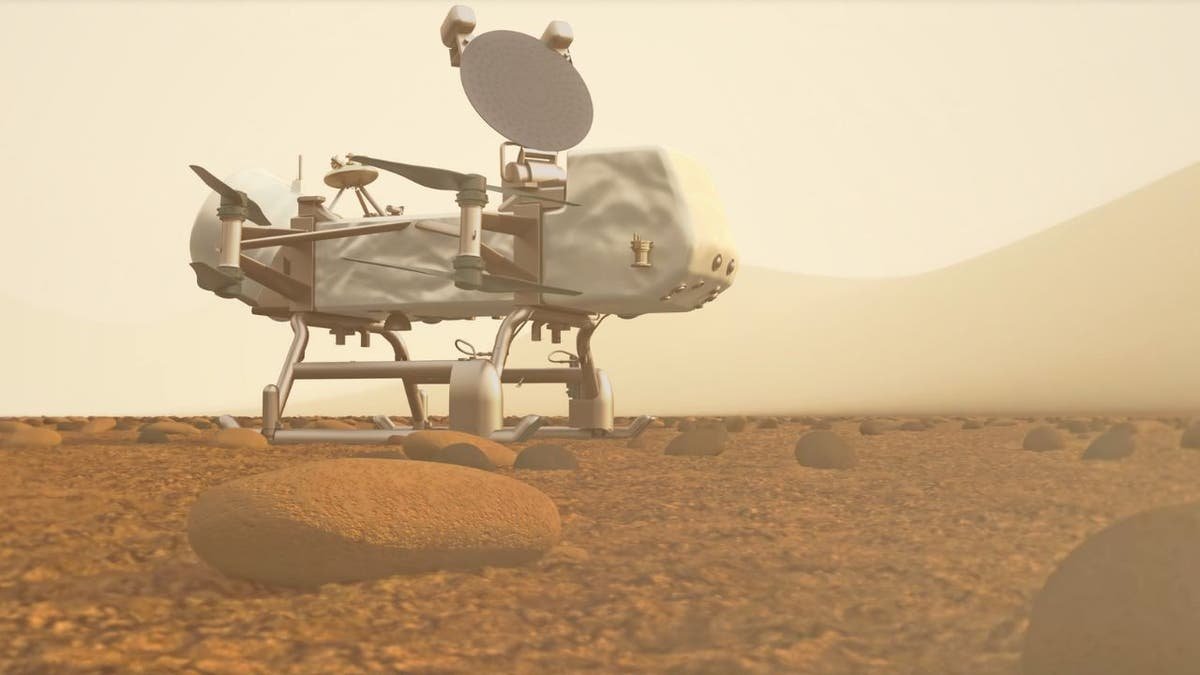
Artist’s concept of the Dragonfly rotorcraft (NASA/JHU-APL)
CLICK HERE TO SET FOX BUSINESS IN CRETE
Mission trip
Despite financial discussions, the mission delay requires a more powerful rocket to ensure Dragonfly’s arrival on Titan. With a budget of $3.35 billion, the mission represents NASA’s commitment to pushing the boundaries of space exploration.
MORE: THE SMALL BUT MIGHTY HELICOPTER THAT WILL MAKE YOU THINK ABOUT THE WAY YOU’LL TRAVEL IN THE FUTURE
Kurt’s outdoor essentials
As NASA’s Dragonfly rotorcraft prepares for flight, it is a testament to human ingenuity and the tireless pursuit of knowledge. This mission may not only reveal the secrets of Titan, but shed light on the origins of life itself. As the world watches, Dragonfly is poised to soar into the history of space exploration.
CLICK HERE TO DOWNLOAD THE FOX NEWS APP
How do you think the findings of the Dragonfly mission to Titan could reshape our understanding of life in space? Let us know by writing to us at Cyberguy.com/Contact.
For more of my tech tips and security alerts, subscribe to my free CyberGuy Report newsletter by going to Cyberguy.com/Newsletter.
Ask Kurt a question or tell us what stories you want us to cover
Answers to the most frequently asked CyberGuy questions:
Copyright 2024 CyberGuy.com. All rights reserved.